¶ Export from Excel to CSV
This task will export Excel data to CSV format. This feature allows you to seamlessly convert Excel files (.xls and .xlsx) into Comma-Separated Values (CSV) files, facilitating data sharing and analysis across different platforms.
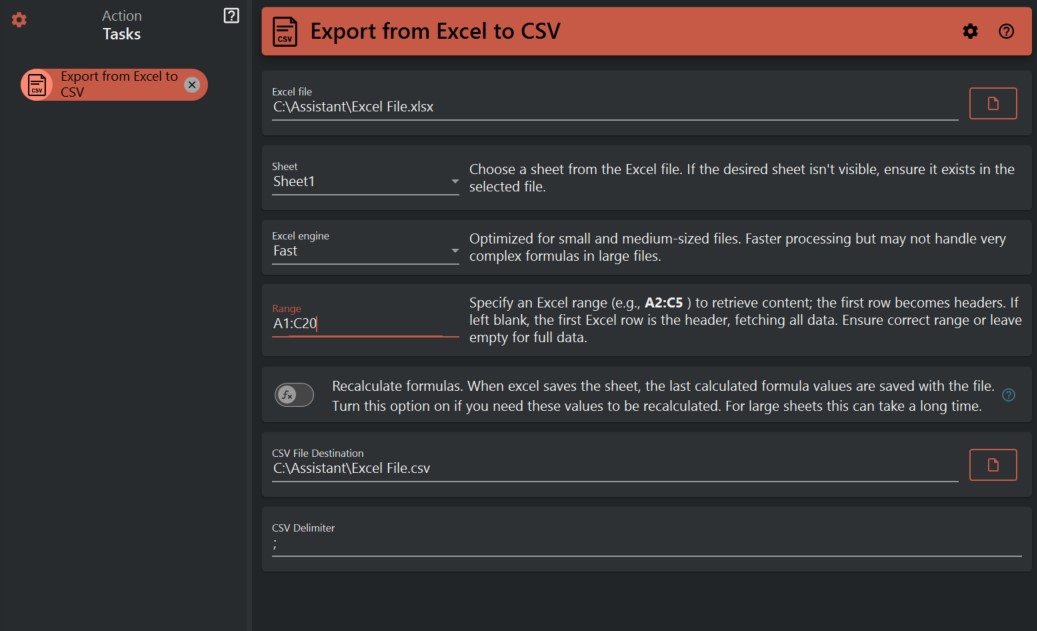
¶ Configuration
¶ Excel File Selection
Start by selecting the Excel file you wish to export. Provide the path to the Excel file on your local system.
¶ Excel Sheet Selection
Choose the specific sheet from the Excel file that you want to export. This allows you to target a specific dataset within the Excel file.
¶ Excel Engine Selection
Choose the Excel engine that best suits your needs: "Fast" or "Standard."
-
Fast Engine: This engine is optimized for small and medium-sized files. It offers faster processing but may not handle very complex formulas in large files.
-
Standard Engine: This engine is designed for larger files or those with complex formulas. While it might be slower, it ensures accurate handling of all formulas.
¶ Range Specification
Specify the Excel range you want to export. For example, entering "A2:C5" will retrieve content from cells A2 to C5, with the first row becoming headers in the CSV. Leaving this blank will fetch all data from the Excel file.
¶ Recalculate Formulas
Select whether you want to recalculate formulas during the export. When Excel saves the sheet, the last calculated formula values are saved with the file. Turn this option on if you need these values to be recalculated. Please note that for large sheets, this can take a significant amount of time.
¶ CSV File Destination
Provide the file path where you want the exported CSV file to be created. Make sure to choose a destination that you can easily access.
¶ CSV Delimiter
Choose the character that will be used to separate values in the CSV file. The default delimiter is a semicolon (;), but you can customize it based on your preferences.